Top 40 Innovations

What better way to celebrate four fabulous decades than to pay tribute to the 40 best and most impactful innovations that have come from CommScope or one of its acquired companies? In 2016, we asked employees to submit recommendations for CommScope’s Top 40 Innovations. We hope you enjoy looking back at what we think are our top innovations—ones that have helped build the world’s infrastructure of today and tomorrow.
Krone LSA-PLUS IDC connector
Year of Innovation: 1978

KRONE LSA-PLUS (or simply KRONE block) is an insulation-displacement connector (IDC) for telecommunications. It is a proprietary European alternative to 110 block, a type of punch block used to terminate runs of on-premises wiring in a structured cabling system. Popularized in the US by NYNEX (now part of Verizon), the KRONE LSA-PLUS system was not only an innovative alternative to 110 blocks but also popular in broadcast systems, where audio interconnections and their associated control systems often used KRONE wiring.
LSA-PLUS is a German acronym:
- Lötfrei (solderless)
- Schraubfrei (screw-less)
- Abisolierfrei (No insulation removal)
- Preiswert (Cost-effective)
- Leicht zu handhaben (Easy to use)
- Universell anwendbar (Universal application)
- Sicher und schnell (Secure and fast)
Unlike 66- and 110-style IDC punch blocks, KRONE contacts can be used with stranded conductors. The contacts use silver to inhibit corrosion. KRONE blocks are also available in versions which can handle frequencies much higher than conventional blocks. The LSA-PLUS was developed in Berlin by The KRONE Group, which was acquired in 2004 by ADC Telecommunications, now part of CommScope.
P3 Design and Process for Coaxial Cable
Year of Innovation: 1978

CommScope-developed proprietary method of producing a physically more robust and lower lost coaxial cable, soon becoming the industry standard worldwide. Most operators in the world have used this cable, or a competitive version, for more than 30 years in CATV MSO networks, allowing high-speed internet delivery to residences/buildings worldwide. Core research from this development also lead to the development of the industry’s first foam FEP dielectrics (Teflon), which contributed to the early success of CommScope’s Enterprise business.
QR cable
Year of Innovation: 1980

QR cable is a patented coaxial design with a foam core, adhesive, thin wall aluminum outer shield and bonded jacket that features superior reliability and flexibility over any other trunk and distribution cable. Developed by CommScope to provide low RF attenuation and integrate easily with existing plant cable, QR cable meets the increasing demands of modern broadband networks. The QR cable features a copper-clad aluminum center conductor that's larger than conductors found in other cables. The QR dielectric is a closed-cell polyethylene that's compressed during the swaging process, which allows for exceptional bending. The QR shield is formed through a unique process where precision tape is continuously roll-formed around the core and welded through RF induction. Then, the QR cable is fitted with a tough outer jacket that resists sunlight, moisture and extreme temperatures. The QR process technology lead the way to the development of the Cell Reach product line and CommScope’s wireless division.
Structured Cabling Systems
Year of Innovation: 1983
Developed as the AT&T Premises Distribution System and later branded SYSTIMAX, this system included all the cabling, wire and associated equipment and apparatus necessary to provide service from the network interface to the information outlet at the work location or communication device within the customer premise. It has evolved to today’s complex network architectures for the intelligent building, data center and a series of other networks required by customers.
Fast Fourier Transform Analysis of Manufacturing Process
Year of Innovation: 1985
Never patented and widely held secret for many years, this technology—which was developed largely over a 10 year period—permitted the real time detection of process machine components which were contributing to the reduction of transmission SRL properties. With literally hundreds of machine components in a single process line, this technology permitted immediate identification and remediation of worn or improperly adjusted machines and machine components. By doing so, scrap levels were dramatically reduced, and the production and inventorying of "off spec" product was also greatly reduced. It permitted the establishment of higher industry standards which were all but impossible to economically produce by existing producers and potential start-ups. The technology started development in the early 1970s with ultralow frequency analog techniques, but the advent of lower cost computer technology led to CommScope applying single channel, digital, FFT process analysis from time to the frequency domain. By the early- to mid-1980s, CommScope had developed its own proprietary equipment for multichannel (50 ch) supervision of the factory.
Digital Signal Cross-connect
Year of Innovation: 1985
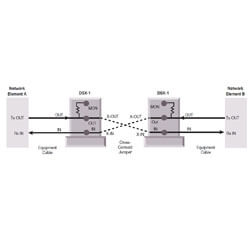
The Digital Signal Cross-connect, or DSX, is a value-added product based on expertise making telephone jacks, a core competency of what was then ADC Telecommunications. For the greater part of two decades following the breakup of the Bell System, the many variations of these two product lines were the growth engine of ADC. ADC became the leading supplier of DSX to the telecommunications industry and its sales allowed investment in the development of the fiber optic products which comprise the majority of our business today.

Tightly Twisted LAN cables
Year of Innovation: 1987-1988
Nearly 30 years ago, an innovative group of cable designers within the copper cabling division of AT&T (now part of CommScope) discovered that twisting conductors together very tightly would maintain the mechanical helical structure and minimize conductor nesting in cables. This dramatically improved the level of isolation between the pairs without necessitating shielding. The unshielded twisted pair cables became known as “data grade UTP” and were standardized as Category 5e in global standards for use in local area networks (LAN) and other applications. Our cable designers and manufacturing teams have continually advanced twisted pair technology to support ever higher data rates.

Extend-A-Cell Repeaters
Year of Innovation: 1987
Repeaters that enabled cellular operators to provide coverage with lower cost installations without requiring backhaul. This Allen Telecom development established repeaters as standard elements in wireless networks. It generated more than $500 million in revenue and made Allen Telecom, which bought Decibel, Mikom, Tekmar, Forem and eventually was bought by Andrew.

Distributed Antenna System Solutions
Year of Innovation: 1989
This development by Decibel Systems (later acquired by Andrew) enabled the neutral host distribution of cellular network signals and became the default method for providing indoor wireless coverage and capacity inside large structures and outdoor venues. Subsequent innovations included digital transport, outdoor DAS, the first digital point-to-multipoint DAS and the first direct CPRI interface to DAS systems.

FiberGuide Fiber Management System
Year of Innovation: 1989
CommScope pioneered fiber cable management with the invention of FiberGuide. FiberGuide provides routing paths and optimal cable management that organize and protect vital fiber optic cables. The system has been designed to assure that the correct fiber bend radius is maintained regardless of which components and sections are assembled. The company holds 148 patents for FiberGuide globally and an additional 54 patents are pending. With FiberGuide, CommScope is the leading global provider of fiber cable management pathways in support of major telecommunications and data center customers.

Single-circuit/Single-element Fiber Management Systems
Year of Innovation: 1992
Fiber management modules (OTIAN, which became FIST in 1997) that became key building blocks of the network elements for an optical access network. It is a management system that allows a customer-based fiber separation level (SOSA with single circuit or single element splice trays) and modules (SASA) with passive optical power splitters for PON networks. Became the global leader in products with ‘positive fiber management’ and gained expertise in optical components (connectors, splitters, WDM). Strong influence in international standard bodies like IEC, ITU-T and Cenelec. Author of many published standards. A later innovation, Low Attentuation Interconnects, enabled CommScope to be a leader in fiber with high performance, ready for the future in all areas of the network.
Outdoor Plant Closure Solutions
Year of Innovation: 1992
Innovations such as heat shrink technology, gel-under-compression sealing and elastic sealing have enabled telecom carriers to protect and seal the outside plant connections from the environment in a simple and reliable way. Heat shrink became the core technology for the majority of the Raychem business in the 1980s and 1990s, and became the global de facto standard for protecting copper splices underground. Gel seals are currently the preferred sealing method for the majority of our fiber optics closures, gradually replacing heatshrink technology. They give a significant competitive advantage over traditional sealing methods that rely on rubbers, mastics or reactive resins.

GeoLENS location estimation system
Year of Innovation: 1992
GeoLENs® Location Measurement Unit (formerly Geometrix™) was a network overlay mobile location system for computing the location of mobile phones. It involved sensors being deployed at cell sites making precise signaling measurements and passing these on to a geolocation control system for location computation. The system was deployed in a 99.999% high availability redundant architecture for multiple cellular carriers. CommScope manufactured and deployed sensors at more than 20,000 cell sites for a variety of US wireless operators, and thousands of emergency callers on wireless devices were found every day. It was the first system ever to deliver a mobile location of a live 911 call to a public safety access point. This innovation paved the way for the location systems and services enjoyed today, common in emergency and commercial applications.
Smart Cell
Year of Innovation: 1994
Smart Cell enabled the use of the same mobile phone for public and private networks. It represented the first implementation of a base station by a CommScope company. It is believed to have been one of the first wireless products for the enterprise, enabling companies to install wireless communication in their premises without the requirement for a different handset than used outside of the premises.

The ODF Family
Year of Innovation: 1995
The Next Generation Frame was the first function-designed high-density ODF. Leveraging sliding adapter pack technology and innovative cable management, the NDF enabled customers to reduce floor space while improving accessibility. The NGF drove updates to the industry standard and broad market acceptance established ADC as the leader in telecom ODFs. It also led to the development of the NG3 and NG4 ODFs, which combined with NGF have contributed more than $500 million in direct revenues.

Base Station Antenna Polarization Diversity
Year of Innovation: 1995
CommScope has continuously developed new technologies and techniques for adding arrays and enabling multiple radio bands to be supported in base station antennas. It started with the MAR dual pole/dual base band antenna element that led to the first dual band BSA, which first enabled high and low band dual pole antenna arrays to be housed in the same size radome as a standard low band radome. By adding more capabilities and bands to the same size antenna, customers save considerable money in rental and leasing fees for towers, while subsequent innovations have led to improved quality, capacity and performance.
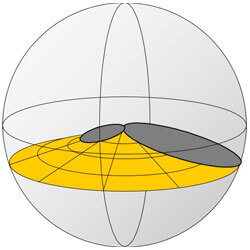
Base Station Antenna Beam Tilting
Year of Innovation: 1995
Base station antennas with RET enable operators to adjust the beam tilt of a base station antenna remotely (for example, from an office location), and the tilt adjustment mechanism (electrical tilt) doesn’t require manual adjustment, which could degrade network performance. Since this CommScope innovation, the wireless industry has widely adopted the use and deployment of RET antennas over the past 15 years and CommScope has shipped billions of dollars of RET-enabled antennas.

Positive Stop RF connector
Year of Innovation: 1995
These radio frequency (RF) coaxial cable connectors enabled network operators to simplify network installations at a reduced cost and with increased reliability. In the manufacturing process, PositiveStop connectors led to several innovations:
First use of machined phosphor bronze contacts rather than heat treated beryllium copper,
First use of a molded TPX insulator rather than machined Teflon,
First use of pre-assembled connector assembly with integral pin,
First use of garter spring clamping mechanism
Laser-optimized Multimode Fiber
Year of Innovation: 1996
It enabled multimode fiber to advance to support 10Gb/s networks that are the foundation of most enterprise data centers today. Further improvements led to OM4. Standardized as TIA-492AAAD, OM4 is optimized for the 25Gb/s per lane applications now emerging. The latest improvement makes OM4 fiber able to support multiple wavelengths with “WideBand” MMF that has just completed standardization as TIA-492AAAE, and is poised to support a range of new applications based on SWDM (short wavelength division multiplexing) to keep multimode cabling capable of delivering the lowest cost solutions. In short, these innovations have allowed multimode fiber to be a significant differentiator for CommScope by offering value to customers while extending MMF’s life cycle by at least 20 years. The revenue stream from these innovations is measured in the billions of dollars, and these fibers are referenced as recommended media in all of the Ethernet and Fibre Channel applications standards since 2002.
Category 6 and Category 6A Cabling and Connectors
Year of Innovation: 1996-97
The breakthrough of multi-stage electrical compensation technology enabled CommScope to be first to market with a Category 6 solution, providing enhanced future proofing to customers and enabling a multi-billion dollar market. To enable industry growth, CommScope actively licensed the technology to others in the industry. First developed in the mid-1990s, this product line continues to generate considerable sales revenue and has led to many patents in the field of cable and connector design.
SureFlex coax jumpers
Year of Innovation: 1998

SureFlex coax jumpers are manufactured using a patented process that utilizes a 360-degree lead-free solder joint to physically bond the connector to the jumper. This highly controlled manufacturing process produces a premium cable assembly that delivers higher RF performance, consistent reliability and outstanding durability. Each assembly is individually tested and guaranteed for exceptional electrical performance and superior weather resistance. And because SureFlex cable assemblies are pre-manufactured, they arrive on-site ready to go. You save valuable time and potential connection error. The SureFlex process is used on all CommScope cable assemblies and for nearly two decades has been recognized as a leading product for RF performance in the wireless industry. As focus in the industry has moved towards high PIM performance products, so has the SureFlex process with the introduction of new IP in 2013 and the recent release of the industry’s first D-Class (Dynamic PIM) rated cable assembly products.
Dual Reflector Antenna Feed—Microwave
Year of Innovation: 1998

Up until this innovation, all microwave antennas (including the very early ValuLine products) used fabricated waveguide feeds requiring craft skills to assemble and then manually tune. This innovation enabled the high volume assembly of microwave feed systems and transformed the need to tune to a purely verification test. In doing so, it allowed substantial reductions in cost as well as being the precursor to the more modern feed systems in use today.
SnapStak hanger
Year of Innovation: 1999

SnapStak hangers are stackable, snap-in coaxial cable hangers that are easy to use, reducing installation time and cost. When cellular network builds picked up steam in the late 1990s, towers were getting too full to handle more cables on the tower face. Development of this hanger by Andrew Corporation (now part of CommScope) allowed cables to be stacked vertically, which increased cable capacity on the tower and changed the installation paradigm in the industry. Stackable up to three deep when securing thinner cables, these innovative hangers feature retention tabs on the spring fork, which holds cables in place yet yields to tower movements and absorbs vibrations. Made from stainless steel, SnapStak provide exceptional reliability and durability, even in the most corrosive environments or punishing weather conditions. It became the predominant cable hanging solution in the wireless industry. Andrew, CommScope and its licensed partners have sold millions of these hangers since their release.
Modal Decomposition Test Set, Channel/Link Simulation Software and Path Analysis Toolkit
Year of Innovation: 2000
Modal decomposition test set allows us to measure individual cabling components such as cable, cordage and connection (mated plug and jack) separately, then cascades them using a pre-determined configuration mathematically. A sizable number of simulations (more than 1,000) can be done within a short period of time. This powerful simulator allows CommScope to assess the link and channel performance much more accurately than what the cabling industry has adopted at this time. Path analysis toolkit is utilized to reduce the number of prototype iterations by mathematically changing the property of the targeted connecting hardware. The test set together with the software enable us to quickly and accurately assess the electrical performance of copper cabling solutions, reduce the number of prototype iterations and provide a statistical base for our performance claims. The major impact to the industry is to reveal the importance of mode conversion parameters (balance) to the design of a Cat-6A UTP cabling system. TIA and ISO/IEC did not treat the balance terms seriously until we showed them our findings.
iPatch Automated Infrastructure Management system
Year of Innovation: 2001

Development and customer demand of iPatch enabled CommScope to be the top provider of automated infrastructure management (AIM) systems for the past 10 years. iPatch, now branded as imVision) also was used as a blueprint in defining the ISO/IEC 18598 standard for AIM systems. It combines intelligent hardware and software to provide users with unprecedented visibility and control over their network connectivity. Through a Web-based graphical user interface (GUI), users can document and monitor the cabling infrastructure as well as track the presence and locations of all connected networked devices in real time.
Fiber Distribution Hub and Splitter Module
Year of Innovation: 2003

The development of the FDH was a key enabler for the growth of Fiber-to-the-Home networks. The OSP cross connect cabinets that were available prior to the FDH did not lend themselves to be properly configured for FTTH. The FDH was designed to be FTTH specific, providing a secure OSP interface for fiber splitters and distribution. Being a key supplier to the major network providers during the explosive FTTH rollout provided critical revenue during a challenging business environment. The current CommScope FDH products incorporate many innovations from legacy acquired companies such as ADC; a true hybrid of technology from multiple sources that has been infused into the product line. Subsequently developed plug-and-play splitter modules enabled fast subscriber turn-up for reduced operating expense, fast installation and delayed capital expenditures for the service provider.
Echo Cancellation Node Repeaters
Year of Innovation: 2003

Digital signal processing was used for filtering of BTS donor or mobile signals, to equalize donor link fluctuations by maintaining constant pilot power in the repeater zone, and to cancel the echo between coverage and donor antenna. The Nod-M and the Node-C were band-selective. The Node-G was a GSM channel-selective frequency-hopping following repeater with echo cancellation. Sprint and Telstra have deployed a high number of those repeaters to provide coverage to remote locations with low to medium capacity requirements. The ease of installation and operation was highly commended by the customers. Repeater deployment was simplified significantly as the antenna isolation was no longer a critical parameter for the repeater site. This product established the digital signal processing within RF repeater and DAS systems where signal analysis was enabling the installation of the systems without the need of any external measurement equipment. The performance of the echo-cancellation is still as good or better than other commercially available products. The technical innovation and market success of this product laid the foundation for successor digital filtering and distribution products like the Node-A, Node-AM, and ION-E.
Twisted Pair Cable Modulation
Year of Innovation: 2003
As transmission rate objectives on twisted pair cables continued to increase, the coupling between pairs in adjacent unshielded cables became the critical new impairment. CommScope engineers discovered that adding modulation to the twist and strand of a cable along its length would break up systematic coupling patterns and thereby dramatically reduce the cable-to-cable coupling or alien crosstalk. Precisely controlled modulation improves the alien crosstalk while preserving and even improving other electrical parameters. This patented technology was instrumental to extend the data rate capacity of unshielded twisted pair cables from 1 to 10 Gigabits per second for lengths up to 100 meters. Modulation technology has also been extended to other twisted pair cables in our global factories enabling reduced size, complexity and cost compared with competitive products.
AMP TWIST Jack with Integrated Blades
Year of Innovation: 2005

The AMP TWIST shielded and unshielded modular jacks, with integrated cutting blades and wire lacing fixture, simplified the copper wire lacing process and dramatically sped up line termination. By enabling all wires to be cut at once, it established the fastest installation available in the market at the time.
InstaPATCH 360
Year of Innovation: 2005

InstaPATCH 360 MPO-Based Pre-terminated Fiber System with Method B architecture is primarily used for data center fabric applications. Built around pre-terminated panels, InstaPATCH 360 is a comprehensive, modular fiber connectivity solution that includes patch panels and shelves, individual modules, trunk cables, ruggedized fan-outs, array cords and fiber patch cords. It is a modular fiber connectivity solution that enables installers to simply and quickly connect system components together, ultimately resulting in improved density, performance and reliability. Within a year of its introduction, this architecture was adopted by the standards bodies because it immediately solved the design, implementation, and migration issues associated with the other proposed Multi-Fiber Push On (MPO) connectivity methods, now known as Methods A & C. It provides customers with blanket duplex and parallel application support, application distance support beyond standards, ease of design and use, and a clear migration path through multiple levels of application speed. CommScope is clearly associated with Method B in the standards bodies and market, enabling data centers to continue to handle the vast amounts of data required now and into the future.
MPO fiber assemblies with round cordage
Year of Innovation: 2005
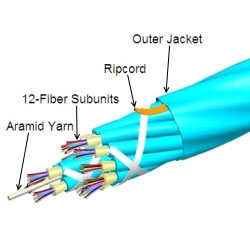
These patented assemblies facilitate the termination of round cable with loose fibers onto Multi-fiber push-on (MPO) connector ferrules, displacing flat ribbon based cable assemblies in the plug and play data center environment. This solution enabled efficient routing of MPO-based cable architectures in densely populated fiber distribution apparatus in data centers, compared to restrictive routing requirements for ribbon-based cable solutions. Direct MPO termination onto this new style cordage eliminated extended ribbonization prior to termination, and also eliminated loose-fiber furcation necessary to transition from legacy loose-fiber cable designs to the MPO connector. Both increased the efficiency of factory terminations, as well as improving installation with a more flexible cable. The loose-tube design also facilitated the introduction of CommScope’s integrated Cable Mounting/Pulling Grip Gland, providing an interface for pulling and securing the assembly in the data center, as well as the unique ability in the industry to change the breakout leg lengths of the assembly after installation, in the field by the end user. The PMP-style loose tube cordage and related Round Boot MPO termination are widely accepted, and copied, in the industry.
Node AM In-Train repeater
Year of Innovation: 2006

The Node AM In-Train Repeater was developed in follow to the MIRT analog RF repeater for in-train wireless coverage. This fully digital platform supports sophisticated features such as gain trailing – the capability to change very rapidly the signal gain of each operator independently as the train moves at 250 km/hour. It also can change configuration and settings based on location detection, for instance changing the complete configuration of the frequency band as the train crosses a border from one country to the neighboring country. CommScope is the leading provider of in-train repeater solutions and enables commuters and travelers to enjoy superb wireless coverage within the coaches of trains.
RapidReel
Year of Innovation: 2007

CommScope pioneered rapid cable deployment with the invention of RapidReel Cable Spool deployment technology. We have been granted many patents for RapidReel Cable Spool, and we continue our innovation with more patents pending. We are the leading global provider of fiber cable management and are the preferred vendor for major telecommunications and data center customers. RapidReel Cable Spool deployment technology provides the customer with the right length of cable all the time, requires minimal installer planning, and significantly reduces installation time.
MPOptimate
Year of Innovation: 2008

This family of products contains connectors, trunks and fan-out cable assemblies with leading optical performance. This performance was achieved by conducting computer modeling to hone in on the most optimal fiber and ferrule dimension/tolerance that allows 100% physical contact when two connectors are mating together. This innovation enables superior optical performance for high-speed and mission-critical data center applications. With such a low insertion loss performance, MPOptimate (LLC) connectors provide customers the maximum flexibility in terms of cabling design for a modern data center. Most of the high-speed applications reduce the allocated power budget of the cabling to accommodate the increasing complexity of the transceiver design. The MPOptimate (LLC) solution gives the design freedom back to the customer—one can deploy more administrative points such as cross-connect and inter-connect in the fiber link without sacrificing the overall system performance. The growth from 10 to 40 and 100Gb/s could be done by changing the patch cords and/or cassettes but maintaining the trunk cabling. This innovation enabled CommScope to become a leader in high-performing, future-ready products in the data center.
Singlemode connector advancements
Year of Innovation: 2008

This Dual ID ferrule project improved the interface between fiber optic cables and connectors to reduce fiber breakage, especially due to thermal stress. The Dual ID ferrule solved a failure repeatedly seen in environmental qualification tests. Fibers were breaking in high humidity environments because standard ferrules had a design that could damage fibers during insertion. Developed by ADC (now part of CommScope), the Dual ID ferrule prevents this fiber damage and eliminated testing failures. The Dual ID ferrule provides a high degree of reliability to products deployed in outside plant FTTX networks, which deploy millions of connectors in uncontrolled environments, making connector reliability critical in network reliability. Also contributing to connector reliability are the patented ferrule anti-rotation geometries used in conjunction with Dual ID ferrules. Angled connector ferrules are highly sensitive to very small rotations. Rotations as small at 0.5° can result in loss of fiber physical contact, which would affect network provider service delivery. Our connector anti-rotation features basically eliminate ferrule rotation and add to the high reliability of connectors in the outdoor network.
Quareo Automated Infrastructure Management System
Year of Innovation: 2009

Quareo technology was developed in response to customer demand for visibility of the part of the network that has always been invisible—the physical layer. Quareo technology is a genuinely revolutionary connection point identification (CPID) technology that brings managed connectivity to the physical layer of the network, enabling an automatic, accurate, and real-time view of a network, from the data center all the way to the desktop. CPID incorporates an integrated circuit placed right on a standard form factor connector, allowing for something that is very akin to a unique ID placed on both ends of the cable. Patch panels with the ability to read the information contained in that chip report information such as unique characteristics of the connection and provide full accountability for each connection point within the network.
DLX Hardened Fiber Optic Connector
Year of Innovation: 2009

The "DLX connector is a small form factor fiber optic connector that is suitable for deployment in the OSP. Hardened connectivity speeds up FTTx deployments because it reduces, if not eliminates, the need for splicing. The small form factor, which is about 2/3 of the size of other hardened connectors, results in smaller terminal footprints. This innovation helped improved our customers' ability to install and deploy by fitting in smaller spaces and having less visual impact. The customer can have a newer generation product with smaller size, improved performance and also many added features. In addition, it also enables the customer to deploy the products on the existing network due to its backward compatibility.
C4000 small cells
Year of Innovation: 2010

The C400"0 series of 3G voice and data residential small cells, sold by Sprint under its AIRAVE brand, was one of the first commercially-successful small cells and one of the highest-volume products in the small cell industry. More than a million have shipped and hundreds of thousands are still in use today. Developed and introduced by Airvana (now a part of CommScope), this was the first small cell to support both CDMA 1xRTT voice and EV-DO data, and it has proved extremely reliable with mean time between failures in the millions of hours. The C4000 has helped ensure subscriber satisfaction by providing “5 bar signals” and proving to be a true plug-and-play solution.
SiteRise Tower Top Solution
Year of Innovation: 2013

SiteRise is world’s first factory integrated and tested tower top solution. It drastically improves quality by eliminating field installation errors and improves speed of deployment by reducing installation time. SiteRise has changed the way customers think about the top of the tower. Factory integration and full system testing have enhanced both quality and speed of deployment, especially in regions with diverse tower rigging skill and experience.

Broadband Radome microwave antennas
Year of Innovation: 2013
Radomes, which are weatherproof enclosures that protect microwave antennas, used to be frequency-specific. For example, a two-foot microwave antenna could require eight different radomes, depending on the frequency band in which they were operating. In addition, each radome required a thickness that had to be very precisely controlled. CommScope’s development of the industry’s first Broadband Radome, using an expanded polystyrene foam base that is virtually invisible to RF, enabled one Radome to replace all these, and the part is not so dimensionally sensitive. This has led to faster delivery times to customers through more efficient production, lower inventory requirements, and the ability to locally configure the radomes without sophisticated equipment or highly-trained staff.
