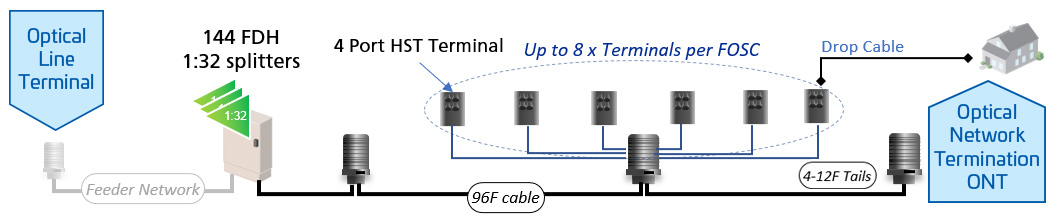
What is an HFC Cable Network?
Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC) is a broadband network architecture used by cable operators to deliver video, data, and voice services. It combines fiber-optic and coaxial cable technologies to efficiently distribute signals from the headend to subscribers.
Key Takeaways
-
Blended fiber and coaxial architecture: HFC networks combine fiber-optic cables for long-distance transmission with coaxial cables for last-mile delivery, offering a balance of speed and flexibility.
-
Efficient signal distribution: Signals travel via fiber from the headend to regional hubs, then convert to radio frequency (RF) for delivery over coaxial lines to homes and businesses.
-
Supports a range of services: HFC networks enable gigabit internet, digital TV, and VoIP services, making them versatile for both residential and commercial use.
-
Cost-effective and scalable: By leveraging existing coaxial infrastructure, HFC allows service providers to expand and upgrade networks without full fiber replacement.
-
Used in diverse broadband applications: HFC is common in cable broadband, small cell backhaul, and fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) expansions, helping providers enhance performance while maintaining legacy compatibility.
How HFC Networks Work
HFC networks transport signals via fiber-optic cables from the headend to regional hubs. From there, the signal is converted into radio frequency (RF) and transmitted over coaxial cables to individual homes and businesses. This hybrid approach balances high-speed fiber transmission with the flexibility of coaxial distribution.
Advantages of HFC Networks
HFC networks provide high bandwidth capacity, scalability, and cost-effective deployment. They support advanced services such as gigabit internet, digital television, and voice-over-IP (VoIP) while leveraging existing infrastructure for efficient upgrades.
Applications of HFC Networks
HFC technology is widely used in cable broadband networks, small cell deployments, and fiber-to-the-premises (FTTP) expansions. It enables service providers to enhance network performance while maintaining compatibility with legacy systems.
Related CommScope Links